
Model strengths vary by
medical domains.
Model strengths vary by medical domains.
A cross-specialty benchmark analysis showing how leading large language models differ in accuracy, reasoning, and specialization across medical tasks and body systems.
Second opinion matters: Towards adaptive clinical AI via the consensus of expert model ensemble
Introduction
Introduction
Medical AI models do not perform uniformly across clinical domains. Each model exhibits distinct strengths depending on the specialty area, task type, and underlying medical complexity.
This page compiles a comprehensive view of model performance across medical tasks, body systems, and question types, based on Sully’s benchmarking of leading LLMs.
Medical AI models do not perform uniformly across clinical domains. Each model exhibits distinct strengths depending on the specialty area, task type, and underlying medical complexity.
This page compiles a comprehensive view of model performance across medical tasks, body systems, and question types, based on Sully’s benchmarking of leading LLMs.
Why domain-level variation exists
Why domain-level variation exists
Why domain-level variation exists
Even state-of-the-art models show substantial variability across specialties due to differences in:
Even state-of-the-art models show substantial variability across specialties due to differences in:
Depth of domain-specific medical knowledge
Depth of domain-specific medical knowledge
Requirements for multi-step reasoning vs. factual recall
Requirements for multi-step reasoning vs. factual recall
Model design (generalist vs. domain-trained)
Model design (generalist vs. domain-trained)
Variances in training corpora and clinical content familiarity
Variances in training corpora and clinical content familiarity
Performance
Performance
01
01
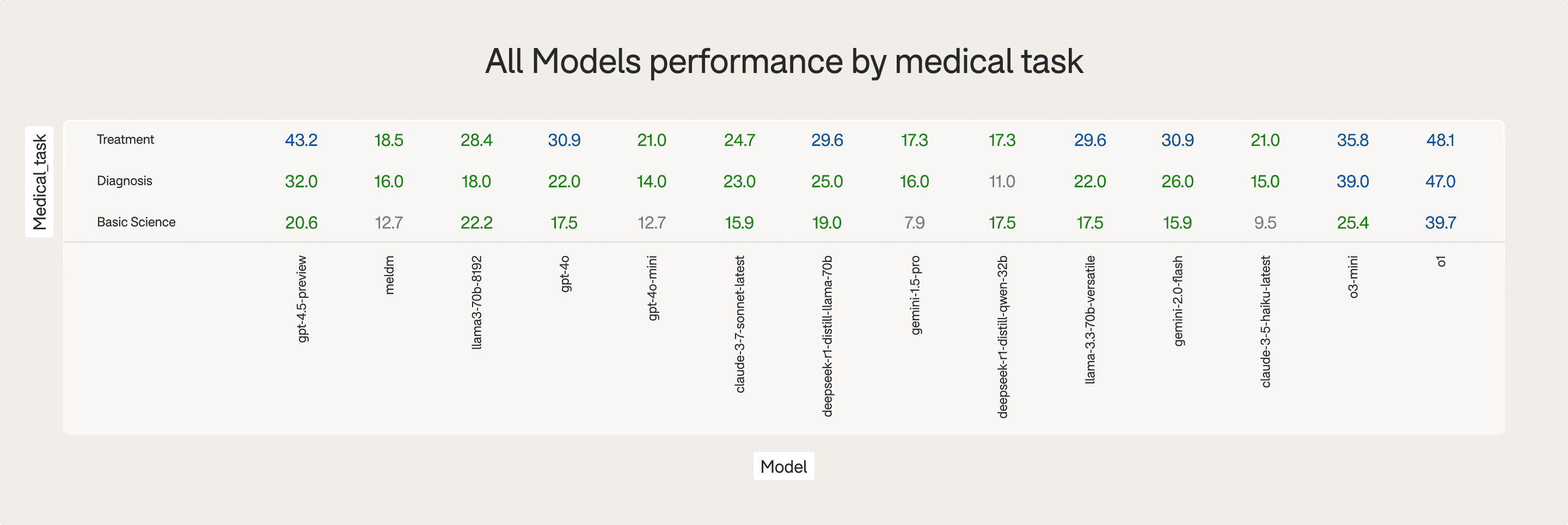
By medical task (Diagnosis, treatment, basic science)
By medical task (Diagnosis, treatment, basic science)
Benchmarks reveal significant differences across task types:
Diagnosis: Best handled by O1 and O3-MINI
Treatment: GPT-4.5-PREVIEW shows specialty strength
Basic Science: Few models exceed 30% accuracy; tasks remain the hardest


02
02
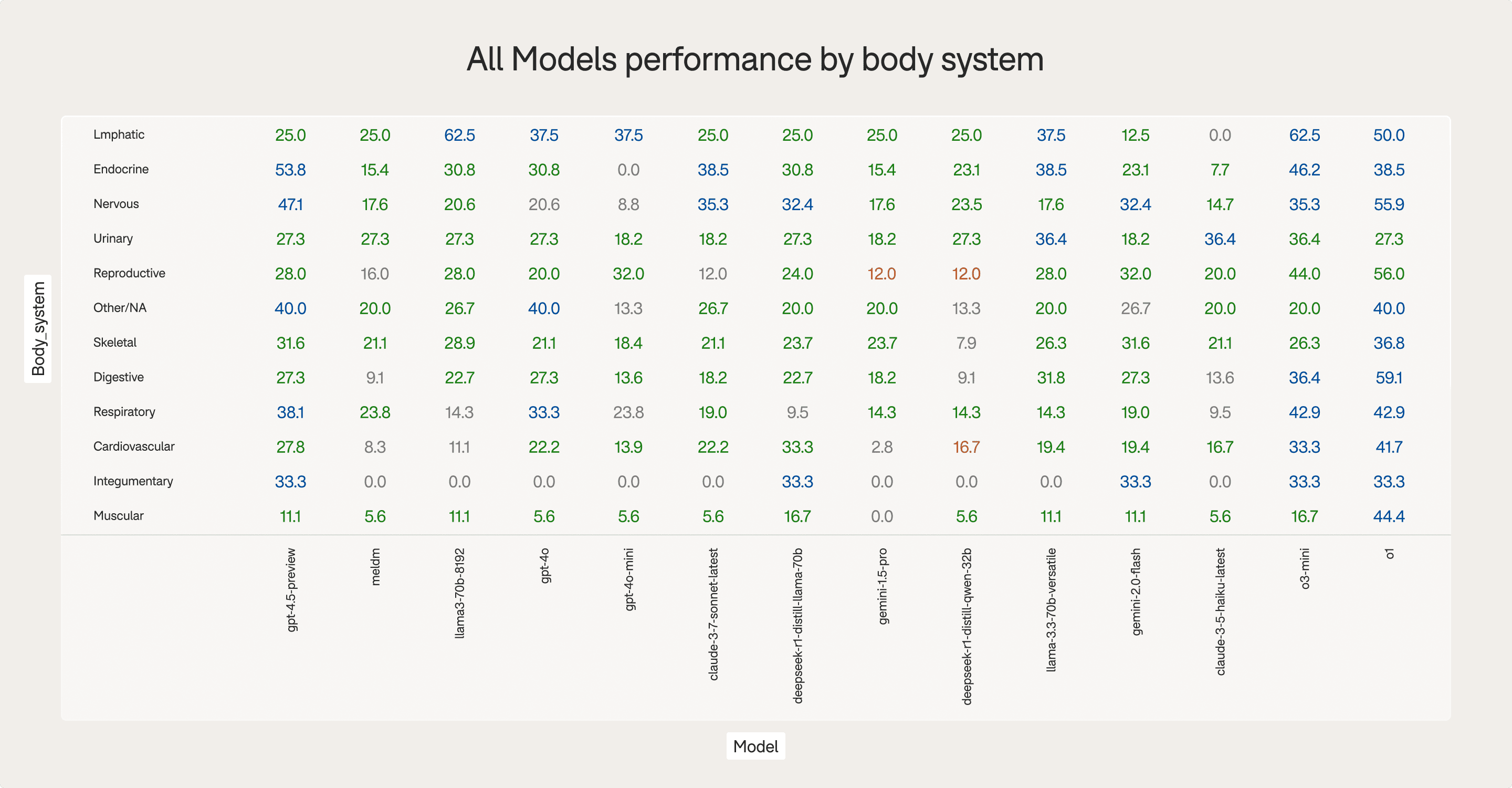
By body system
By body system
Model strengths diverge sharply depending on the clinical system involved.
Examples:
Lymphatic: O3-MINI reaches 62.5% (top model result)
Digestive: O1 peaks at 59.09% (best system for O1)
Endocrine: GPT-4.5-PREVIEW achieves 53.85%
Respiratory: O3-MINI at 42.9%


Standout specialty-specific wins
Standout specialty-specific wins
Standout specialty-specific wins
Some combinations reach exceptional accuracy (>90th percentile)
Some combinations reach exceptional accuracy (>90th percentile)



This illustrates how specialist-focused models or ensembles can outperform generalized models in meaningful clinical niches.
This illustrates how specialist-focused models or ensembles can outperform generalized models in meaningful clinical niches.
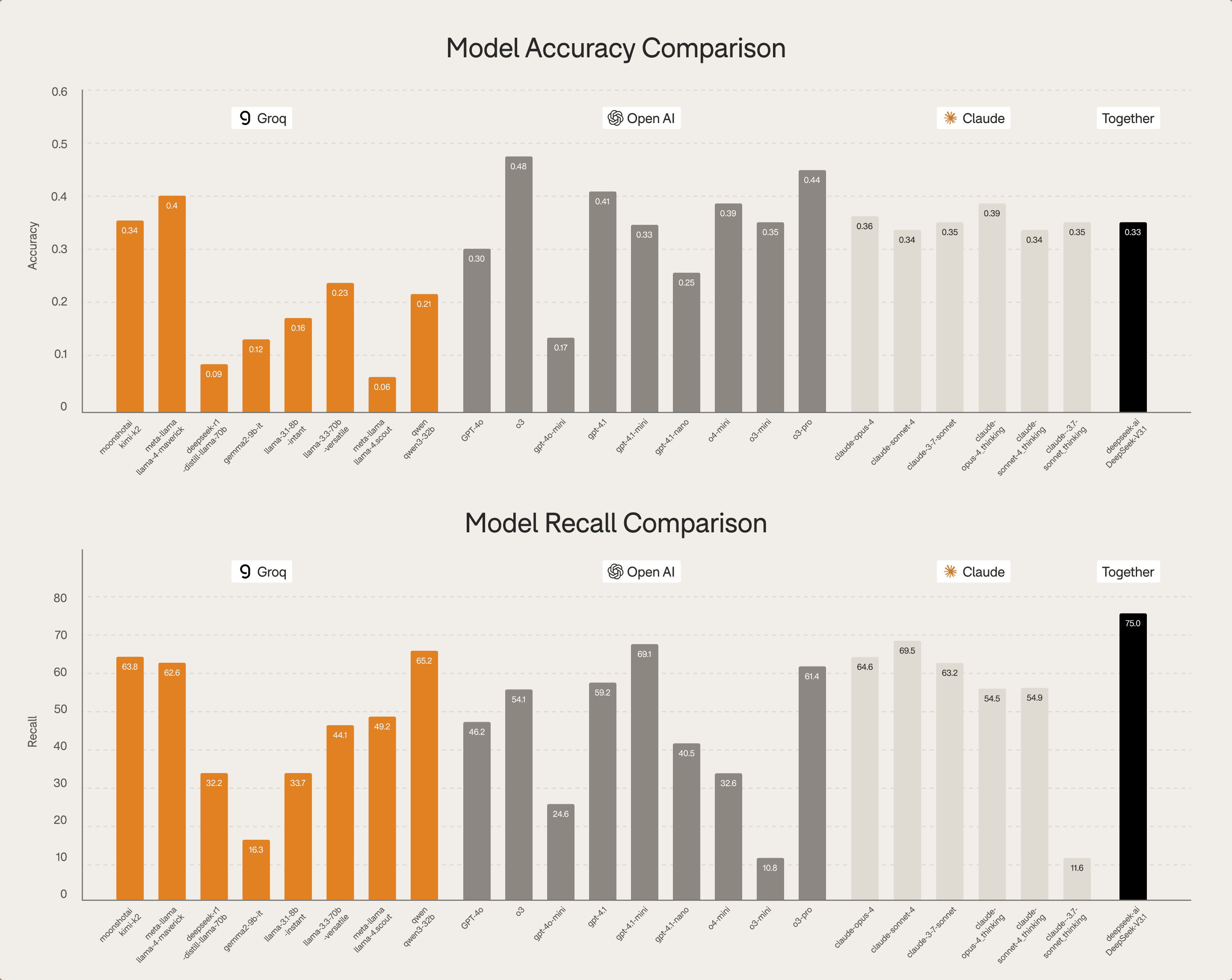
Cross-vendor comparison
The fragility of clinical
AI systems
Cross-vendor comparison
Groq models show competitive recall
OpenAI models demonstrate strong accuracy in higher-tier models
Claude models display consistent but mid-range performance
Together (Deepseek-distill) peaks well in recall in limited contexts
Groq models show competitive recall
OpenAI models demonstrate strong accuracy in higher-tier models
Claude models display consistent but mid-range performance
Together (Deepseek-distill) peaks well in recall in limited contexts


Key takeaways
Key takeaways
01
01
No model is universally strong specialty strengths vary widely.
No model is universally strong specialty strengths vary widely.
02
02
Ensembles or consensus-based systems outperform single-model setups in specialized tasks.
Ensembles or consensus-based systems outperform single-model setups in specialized tasks.
03
03
Reasoning tasks are generally easier for models than understanding tasks.
Reasoning tasks are generally easier for models than understanding tasks.
04
Basic science knowledge is a shared weakness across models.
04
Basic science knowledge is a shared weakness across models.
05
05
Confidence is not equal to accuracy calibration is still a major challenge.
Confidence is not equal to accuracy calibration is still a major challenge.
06
Vendor performance varies, but even top models leave large gaps in clinical reliability.
06
Vendor performance varies, but even top models leave large gaps in clinical reliability.



Download the full
academic paper.
Download the full
academic paper.
Download now
Resources
© Sully AI 2025. All Rights Reserved.
Epic is a registered trademark of Epic Systems Corporation.
Resources
© Sully AI 2025. All Rights Reserved.
Epic is a registered trademark of Epic Systems Corporation.
Resources
© Sully AI 2025. All Rights Reserved.
Epic is a registered trademark of Epic Systems Corporation.