
Towards Open-Source Foundational Medical Agents
Towards Open-Source Foundational Medical Agents
Introduction
Introduction
The rapid advancement of large language models has transformed healthcare AI, but it has also introduced a critical vulnerability: dependency on closed, proprietary systems. When a foundation model provider updates their weights or inference stack, downstream healthcare applications can experience unexpected quality regressions—often without warning.
At Sully, we've embraced open-source foundational models as the backbone of our medical AI agents. This whitepaper explains why, and how we've developed techniques to match or exceed proprietary model performance while maintaining full control over quality.
The rapid advancement of large language models has transformed healthcare AI, but it has also introduced a critical vulnerability: dependency on closed, proprietary systems. When a foundation model provider updates their weights or inference stack, downstream healthcare applications can experience unexpected quality regressions—often without warning.
At Sully, we've embraced open-source foundational models as the backbone of our medical AI agents. This whitepaper explains why, and how we've developed techniques to match or exceed proprietary model performance while maintaining full control over quality.
The Regression Problem
The Regression Problem
01
01
Unpredictable Quality Changes
Unpredictable Quality Changes
Foundation model providers regularly update their systems—adjusting weights, modifying system prompts, or optimizing inference infrastructure. While these changes may reduce costs or improve general performance, they can have unintended consequences for specialized medical applications.
Through continuous weekly benchmarking across multiple foundation models, we observed measurable quality regressions in proprietary reasoning models. One notable decline coincided with the announcement of an updated inference stack designed to reduce API costs. For healthcare applications where consistency and reliability are paramount, this unpredictability represents a significant risk.
Foundation model providers regularly update their systems—adjusting weights, modifying system prompts, or optimizing inference infrastructure. While these changes may reduce costs or improve general performance, they can have unintended consequences for specialized medical applications.
Through continuous weekly benchmarking across multiple foundation models, we observed measurable quality regressions in proprietary reasoning models. One notable decline coincided with the announcement of an updated inference stack designed to reduce API costs. For healthcare applications where consistency and reliability are paramount, this unpredictability represents a significant risk.
This image shows the results from our proprietary evaluation system showing how note quality regressed over time with a specific focus on decreases in:
Clinical accuracy
Safety
Information architecture
Template adherence
These are run on the same sample set, with the same evaluation, and same foundational model.



02
02
The Case for Control
The Case for Control
When patient care depends on AI-generated outputs, organizations need:
Version stability: Confidence that model behavior remains consistent
Transparency: Understanding of what changes and when
Rollback capability: The ability to revert to known-good configurations
Customization: Fine-tuning for specific clinical contexts
Open-source models deliver all of these capabilities. By running inference on our own infrastructure, we maintain complete control over the AI systems our customers depend on.
Open-source models deliver all of these capabilities. By running inference on our own infrastructure, we maintain complete control over the AI systems our customers depend on.



Benefits of Open-Source Models
Benefits of Open-Source Models
Open-source foundational models offer three primary advantages for production healthcare AI:
Open-source foundational models offer three primary advantages for production healthcare AI:
01
01
Cost Efficiency
Cost Efficiency
Smaller parameter models running on optimized infrastructure dramatically reduce per-inference costs. This makes AI-assisted workflows economically viable at scale—enabling features that would be prohibitively expensive with proprietary APIs.
Smaller parameter models running on optimized infrastructure dramatically reduce per-inference costs. This makes AI-assisted workflows economically viable at scale—enabling features that would be prohibitively expensive with proprietary APIs.
02
02
Lower Latency
Lower Latency
Open-source models can run on specialized hardware—custom LPUs, optimized accelerators, and purpose-built inference chips—delivering response times that enhance rather than interrupt clinical workflows.
Open-source models can run on specialized hardware—custom LPUs, optimized accelerators, and purpose-built inference chips—delivering response times that enhance rather than interrupt clinical workflows.
03
03
Scale Infinitely
Scale Infinitely
Without API rate limits or third-party dependencies, open-source deployments scale predictably with demand. This is essential for healthcare organizations processing thousands of clinical encounters daily.
Without API rate limits or third-party dependencies, open-source deployments scale predictably with demand. This is essential for healthcare organizations processing thousands of clinical encounters daily.
04
Improved patient experience
with clear, multilingual guidance across channels.
Bridging the Gap: Ensembling and Consensus
Bridging the Gap: Ensembling and Consensus
Overview
Overview
Multi-Model Ensembling
Multi-Model Ensembling
Aggregated Consensus
Aggregated Consensus
Open-source models, particularly smaller ones, may individually lag behind the largest proprietary models in complex reasoning tasks. We address this limitation through two key techniques:
Open-source models, particularly smaller ones, may individually lag behind the largest proprietary models in complex reasoning tasks. We address this limitation through two key techniques:
Rather than relying on a single model, we orchestrate multiple models working in concert. Each model contributes its strengths, and the ensemble produces outputs that exceed what any individual model could achieve alone.
Rather than relying on a single model, we orchestrate multiple models working in concert. Each model contributes its strengths, and the ensemble produces outputs that exceed what any individual model could achieve alone.
For high-stakes clinical decisions, we implement consensus mechanisms where multiple models independently evaluate the same input. Agreement across models increases confidence; disagreement triggers additional review or escalation.
These techniques, combined with systematic optimization to identify the best configuration of open-source models for each use case, allow us to deliver production-quality medical AI without sacrificing control or predictability.
For high-stakes clinical decisions, we implement consensus mechanisms where multiple models independently evaluate the same input. Agreement across models increases confidence; disagreement triggers additional review or escalation.
These techniques, combined with systematic optimization to identify the best configuration of open-source models for each use case, allow us to deliver production-quality medical AI without sacrificing control or predictability.
Performance Benchmarks
Performance Benchmarks
Performance Benchmarks
The following benchmark compares latency, cost, and accuracy across models for a medical coding use case:
The following benchmark compares latency, cost, and accuracy across models for a medical coding use case:
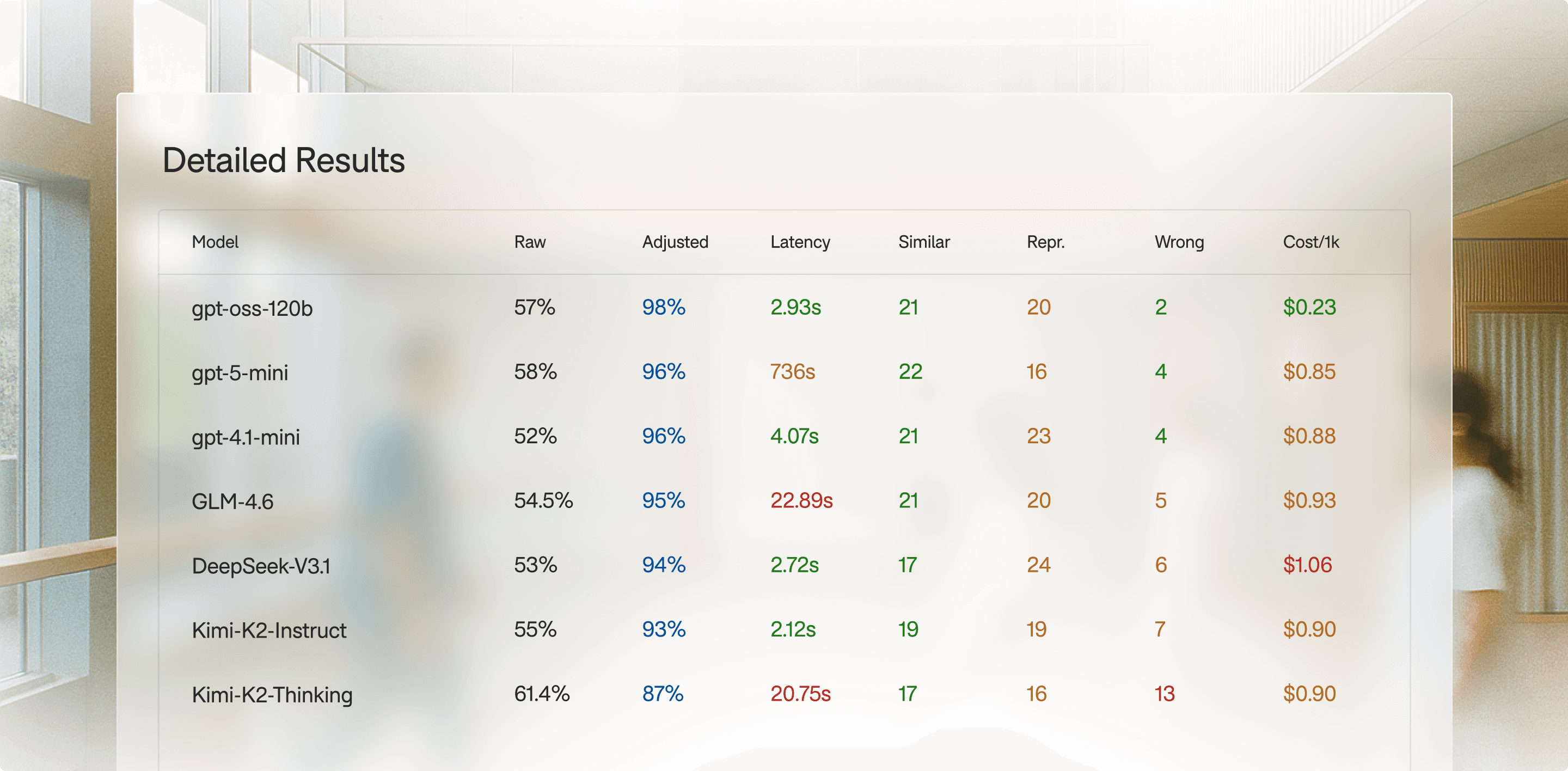


Our benchmarks demonstrate that properly optimized open-source models can achieve competitive accuracy while delivering significant improvements in cost and latency.
Our benchmarks demonstrate that properly optimized open-source models can achieve competitive accuracy while delivering significant improvements in cost and latency.
Conclusion
Conclusion
Conclusion
The path to reliable, scalable healthcare AI runs through open-source. By embracing open models and developing sophisticated orchestration techniques, we've built medical agents that are more controllable, more cost-effective, and more predictable than systems dependent on proprietary APIs.
This isn't about avoiding innovation from foundation model labs—it's about building healthcare AI that organizations can trust and depend on, today and tomorrow.
The path to reliable, scalable healthcare AI runs through open-source. By embracing open models and developing sophisticated orchestration techniques, we've built medical agents that are more controllable, more cost-effective, and more predictable than systems dependent on proprietary APIs.
This isn't about avoiding innovation from foundation model labs—it's about building healthcare AI that organizations can trust and depend on, today and tomorrow.



Download the full
academic paper.
Download the full
academic paper.
Download now
Resources
© Sully AI 2025. All Rights Reserved.
Epic is a registered trademark of Epic Systems Corporation.
Resources
© Sully AI 2025. All Rights Reserved.
Epic is a registered trademark of Epic Systems Corporation.
Resources
© Sully AI 2025. All Rights Reserved.
Epic is a registered trademark of Epic Systems Corporation.